Eğitimler
Smoothing
Bu çizim, çalışan bir ortalamayı hesaplayıp bilgisayara yazdırarak analog girişten tekrar tekrar okunur. Bu örnek, gergin veya düzensiz sensörlerden değerleri düzeltmek için yararlıdır ve ayrıca veri depolamak için dizilerin kullanımını gösterir.
Donanım
- Arduino veya Genuino Kurulu
- 10k ohm potansiyometre
Devre
büyütmek için resme tıklayın
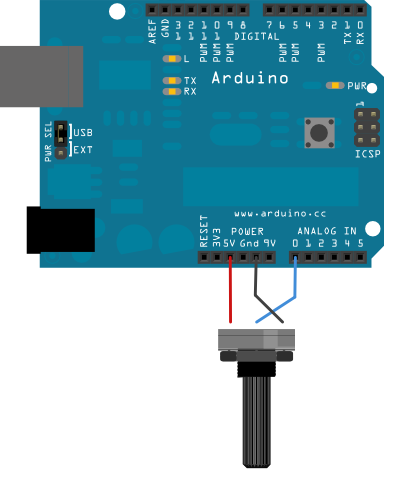
Potansiyometrenin bir pimini 5V'ye, orta pimi analog pim 0'a ve son pimi şasiye bağlayın.
Şematik
büyütmek için resme tıklayın

Kod
Aşağıdaki kod, analog sensörünüzden 10 okumayı diziler halinde sırayla depolar. Her yeni değerde, tüm sayıların toplamı üretilir ve bölünür, bu da daha sonra dış verileri düzeltmek için kullanılan ortalama bir değer üretir. Bu ortalama, diziye her yeni değer eklendiğinde (örneğin, 10 yeni değer beklemek yerine) gerçekleştiği için, bu çalışan ortalamanın hesaplanmasında gecikme süresi yoktur.
Kullanılan dizinin boyutunu değiştirmek, numReadings değerini daha büyük bir değere değiştirerek toplanan verileri daha da düzleştirecektir.
/*
Smoothing
Reads repeatedly from an analog input, calculating a running average and
printing it to the computer. Keeps ten readings in an array and continually
averages them.
The circuit:
- analog sensor (potentiometer will do) attached to analog input 0
created 22 Apr 2007
by David A. Mellis
See Also
- array
- if
- for
- serial
- AnalogInOutSerial- Bir analog giriş pinini okuyun, sonucu eşleyin ve ardından bir LED'i kısmak veya aydınlatmak için bu verileri kullanın.
- AnalogInput- Bir LED'in yanıp sönmesini kontrol etmek için bir potansiyometre kullanın.
- AnalogWriteMega- Arduino veya Genuino Mega kartı kullanarak 12 LED'i birer birer söner ve söndürür.
- Calibration- Beklenen analog sensör değerleri için bir maksimum ve minimum tanımlayın.
- Fading- Bir LED'in solması için bir analog çıkış (PWM pin) kullanın.
