Eğitimler
MasterReader
Bazı durumlarda, birbirleriyle bilgi paylaşmak için iki (veya daha fazla!) Arduino ve Genuino kartı kurmak yardımcı olabilir. Bu örnekte, iki kart I2C senkron seri protokolü aracılığıyla bir Master Reader / Slave Sender yapılandırmasında birbirleriyle iletişim kuracak şekilde programlanmıştır. Bunu başarmak için Arduino'nun Tel Kütüphanesi'nin çeşitli fonksiyonları kullanılmaktadır. Master Arduino 1, benzersiz olarak ele alınan Slave Arduino'dan gönderilen 6 bayt veri istemek ve sonra okumak için programlanmıştır. Bu mesaj alındıktan sonra Arduino Software (IDE) seri monitör penceresinde görüntülenebilir.
I2C protokolü veri göndermek ve almak için iki hat kullanılmasını içerir: Arduino veya Genuino Master kartının düzenli aralıklarla attığı bir seri saat pimi (SCL) ve iki cihaz arasında verinin gönderildiği bir seri veri pimi (SDA) . Saat çizgisi alçaktan yükseğe değiştiğinde (saat darbesinin yükselen kenarı olarak bilinir), belirli bir cihazın adresini ve aa komutunu veya verilerini sırayla oluşturacak olan tek bir bilgi biti karttan SDA hattı üzerinden I2C cihazı. Bu bilgiler - bit bitinden sonra - gönderildiğinde, çağrılan cihaz isteği yürütür ve gerekirse, zamanlama olarak SCL'de Master tarafından üretilen saat sinyalini kullanarak aynı satır üzerinden verilerini geri gönderir.
I2C protokolü, etkinleştirilmiş her cihazın kendine özgü bir adrese sahip olmasına izin verdiği ve hem ana hem de bağımlı cihazların tek bir hat üzerinden iletişim kurması nedeniyle Arduino veya Genuino kartınızın birçok cihazla iletişim kurması (sırayla) mümkündür veya diğer kartlar, mikro denetleyicinizin yalnızca iki pimini kullanırken.
Gerekli Donanım
- 2 Arduino veya Genuino Kartı
- bağlantı telleri
Devre
Ana karttaki pim 4'ü (veri veya SDA, pim) ve pim 5'i (saat veya SCL, pim) köle kartındaki karşılıklarına bağlayın. Her iki kartın da ortak bir zemini paylaştığından emin olun. Seri iletişimi etkinleştirmek için ana kartın bilgisayarınıza USB ile bağlı olması gerekir.
Kartlara bağımsız olarak güç vermek bir sorun teşkil ediyorsa, Master'ın 5V çıkışını slave üzerindeki VIN pinine bağlayın.
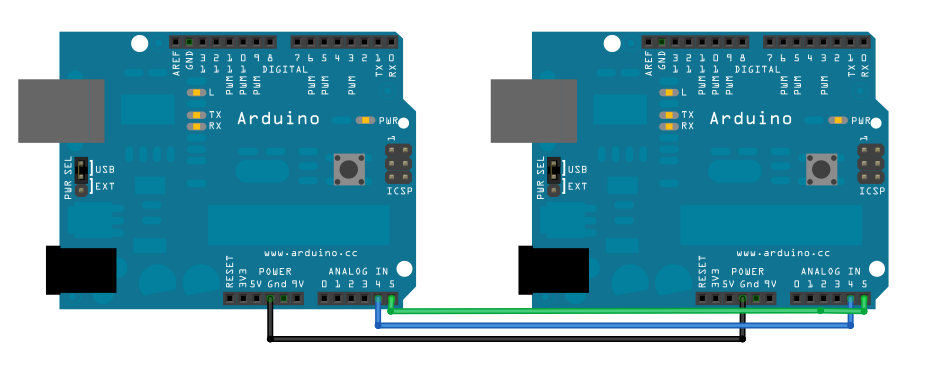
Şematik

Kod
// Wire Master Reader
// by Nicholas Zambetti
// Wire Slave Receiver // by Nicholas Zambetti // Demonstrates use of the Wire library // Receives data as an I2C/TWI slave device // Refer to the "Wire Master Writer" example for use with this // Created 29 March 2006 // This example code is in the public domain. #include void setup() { Wire.begin(4); // join i2c bus with address #4 Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // register event Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output } void loop() { delay(100); } // function that executes whenever data is received from master // this function is registered as an event, see setup() void receiveEvent(int howMany) { while(1 < Wire.available()) // loop through all but the last { char c = Wire.read(); // receive byte as a character Serial.print(c); // print the character } int x = Wire.read(); // receive byte as an integer Serial.println(x); // print the integer } // Wire Slave Receiver // by Nicholas Zambetti // Demonstrates use of the Wire library // Receives data as an I2C/TWI slave device // Refer to the "Wire Master Writer" example for use with this // Created 29 March 2006 // This example code is in the public domain. #include void setup() { Wire.begin(4); // join i2c bus with address #4 Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // register event Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output } void loop() { delay(100); } // function that executes whenever data is received from master // this function is registered as an event, see setup() void receiveEvent(int howMany) { while(1 < Wire.available()) // loop through all but the last { char c = Wire.read(); // receive byte as a character Serial.print(c); // print the character } int x = Wire.read(); // receive byte as an integer Serial.println(x); // print the integer } // Wire Slave Receiver // by Nicholas Zambetti // Demonstrates use of the Wire library // Receives data as an I2C/TWI slave device // Refer to the "Wire Master Writer" example for use with this // Created 29 March 2006 // This example code is in the public domain. #include void setup() { Wire.begin(4); // join i2c bus with address #4 Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // register event Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output } void loop() { delay(100); } // function that executes whenever data is received from master // this function is registered as an event, see setup() void receiveEvent(int howMany) { while(1 < Wire.available()) // loop through all but the last { char c = Wire.read(); // receive byte as a character Serial.print(c); // print the character } int x = Wire.read(); // receive byte as an integer Serial.println(x); // print the integer }
See Also
- Wire.begin()
- Wire.RequestFrom()
- Wire.receive()
- Wire.send()
- Wire.onRequest()
- Wire Library- Tel Kütüphanesi için referansınız.
- DigitalPotentiometer- Analog Aygıtlar AD5171 Dijital Potansiyometre nasıl kontrol edilir.
- SFRRanger_reader- I2C ile arayüzlenmiş bir ultra-sonik telemetre nasıl okunur.
- Master Writer/Slave receiver- İki Arduino, I2C aracılığıyla bir Master Writer / Slave Receiver yapılandırmasında iletişim kuracak şekilde programlanmıştır.
